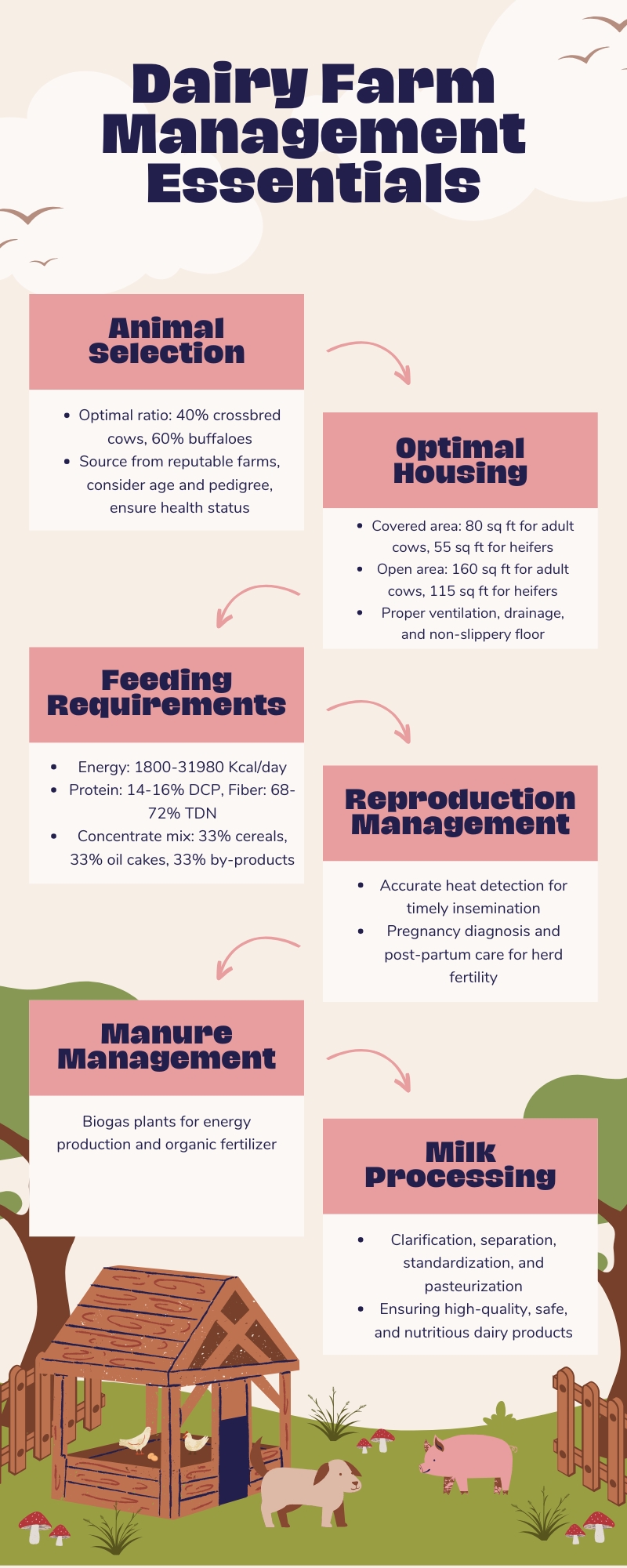
Dairy farming is vital to global agriculture, contributing significantly to food security and sustainable development.
The success of a dairy farm hinges on implementing efficient management practices encompassing various areas, from animal selection to milk processing and marketing.
This article discusses the key elements of dairy farm management, providing farmers and industry stakeholders with the knowledge and insights necessary to optimize their operations.
Key Takeaways:
- Careful selection of healthy, productive foundation stock is crucial for the success of a dairy farm.
- Proper housing design, including adequate space, ventilation, and sanitation, is esse
 ntial for animal welfare and productivity.
ntial for animal welfare and productivity. - Maintaining a balanced and nutritious feeding program tailored to the specific requirements of different animal categories is crucial for optimal milk production.
- Effective reproduction management, including heat detection, timely insemination, and post-partum care, can improve herd fertility and calving rates.
- Utilizing specialized dairy management software can streamline record-keeping, enhance data-driven decision-making, and improve farm efficiency.
- Proper manure management through biogas plants can provide a valuable source of organic fertilizer and reduce waste disposal challenges.
- Understanding milk composition and implementing efficient processing techniques can ensure the production of high-quality, safe, and nutritious dairy products.
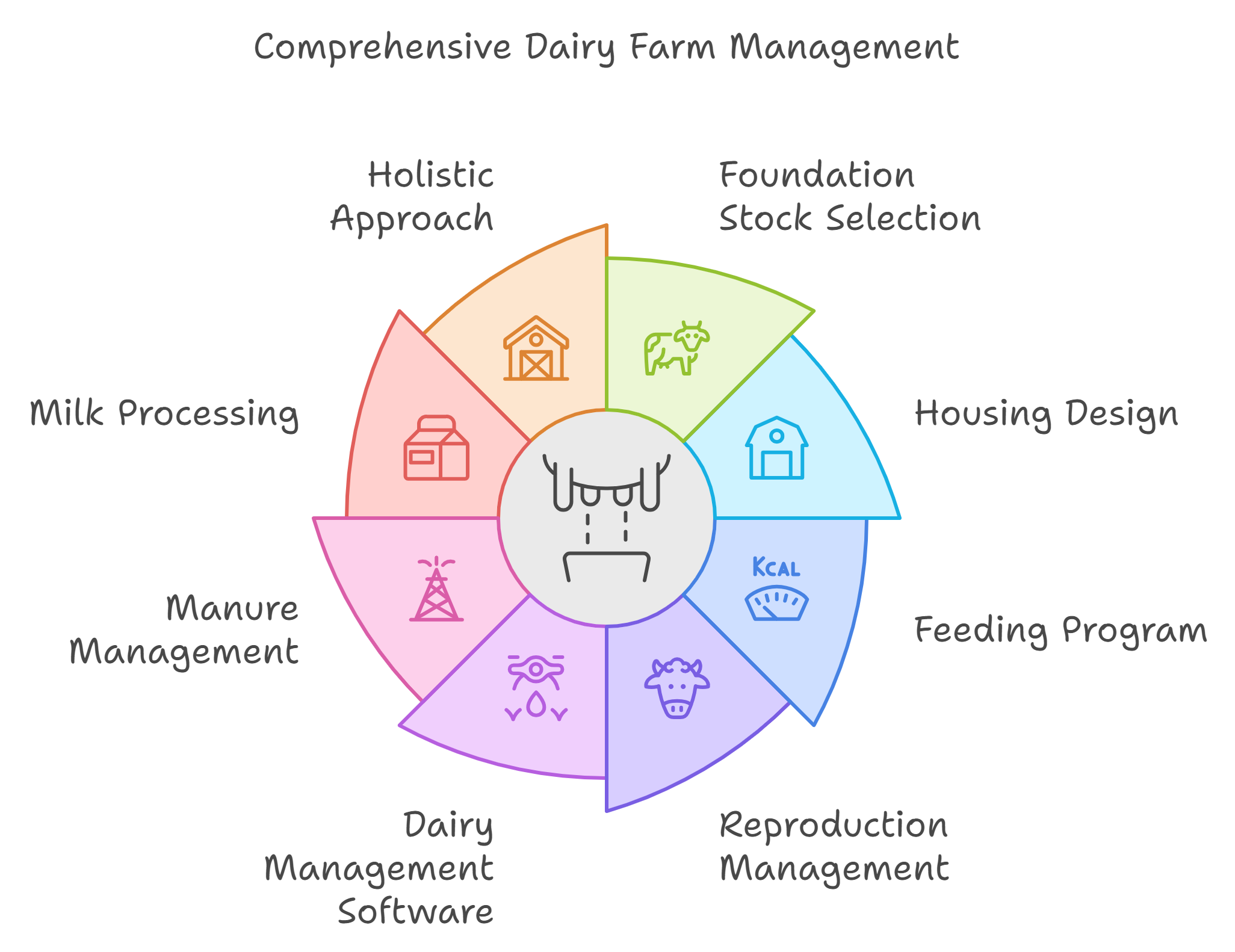
- A comprehensive, holistic approach to dairy farm management is essential for maximizing productivity, profitability, and sustainability in the dairy industry.

Dairy Farm Management Selection of Foundation Stock
The foundation of a successful dairy farm lies in the selection of healthy and productive animals. Farmers can choose between crossbred or purebred cows and buffaloes, with an optimal ratio of 40:60 for cows and buffaloes, respectively. During the selection process, several factors should be considered:
- Source: Animals should be sourced from reputable, organized farms or farmers’ herds to ensure quality and traceability.
- Age and Pedigree: Opt for animals of appropriate age with a known and desirable pedigree to maximize productivity and genetic potential.
- Health Status: Ensure the animals are free from diseases, and vaccinate newly purchased animals to protect the herd’s health.
After the purchase, new animals should be kept under observation for about two weeks before being integrated into the main herd, allowing for a smooth transition and minimizing the risk of disease transmission.

Components of a Commercial Dairy Farm Management
A well-equipped dairy farm should have the following key components:
- Milch Animal Sheds: Dedicated housing for lactating cows and buffaloes.
- Calf Shed: Specialized housing for newborn and young calves.
- Feed Godown: A storage facility for animal feed and fodder.
- Chaffing Area: A designated space for chopping and preparing fodder.
- Milk Collection Unit: An area for collecting, storing, and cooling the raw milk.
- Dispensary Room: A dedicated space for veterinary care and medication storage.
- Paddock: An open-air enclosure for the animals to graze and exercise.
- Drainage System: Proper drainage to maintain a clean and hygienic environment.
- Foot Bath: A disinfectant bath for the animals to walk through, controlling the spread of diseases.
- Store: A storage area for farm equipment, tools, and other supplies.
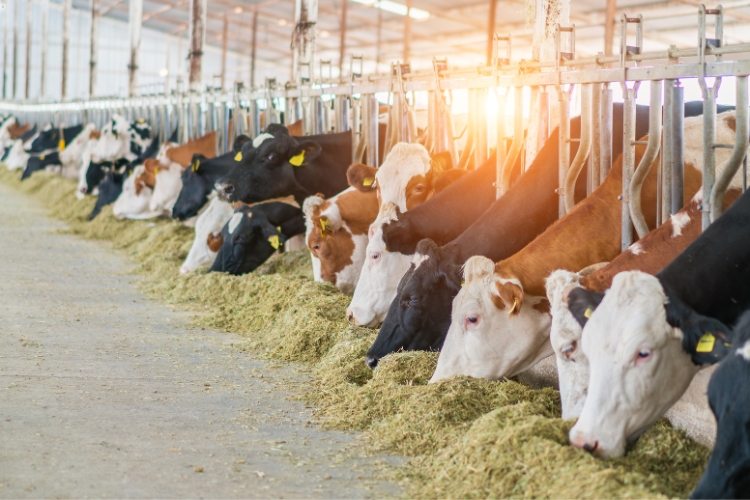

Space Requirements for Animals
Adequate space is essential for the comfort and well-being of the animals. The table below outlines the recommended covered and open areas, feeding manger length, and water trough radius for different animal categories:
| Animals | Covered Area (sq ft) | Open Area (sq ft) | Feeding Manger Length (ft) | Water Trough Radius (ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult Cows | 80 | 160 | 3 | 6 |
| Heifer | 55 | 115 | 2 | 4 |
| Young Calves (<6 months) | 10 | 40 | 1.2 | 2 |
Ensuring the appropriate space for each animal category is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive herd.

Housing Design and Requirements
Dairy barns can be designed in a face-to-face or tail-to-tail system, with the choice depending on the farmer’s preference and available space. The sketch provided in the source illustrates a typical dairy shed for 10 cows. Critical housing requirements include:
- Adequate Space: Providing sufficient space for the animals to move, rest, and access feed and water.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring fresh air circulation to maintain a comfortable and healthy environment.
- Good Slope and Drainage: Proper slope in the floor and an effective drainage system to maintain cleanliness and prevent the accumulation of waste.
- Hard, Non-Slippery Floor: Using a durable, non-slippery floor material to prevent injuries.
- Foot Bath: Placing a foot bath with disinfectants at the gate to control the spread of diseases.
Adhering to these housing design and requirement guidelines can significantly improve the overall well-being and productivity of the dairy herd.

Essential Equipment
A dairy farm of 50 cows typically requires the following essential equipment:
| Equipment | No. | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Tying Chains | 50 | Iron |
| Milking Pails (10 lt.) | 10 | Steel |
| Milk Can (40 lt.) | 7 | Aluminum |
| Milking Machine | 2 | Steel |
| Weighing Balance | 1 | – |
| Sickles | 10 | Iron |
| Brush | 5 | – |
| AI Equipment | 1 | – |
| Veterinary Equipment | – | – |
| Dehorner | 1 | – |
| Branding/Tagging Machine | 1 | – |
This equipment list provides a baseline for the essential tools and machinery required for the efficient operation of a 50-cow dairy farm.

Routine Farm Operations
The day-to-day operations on a dairy farm include:
- Washing and Grooming Animals: Maintaining the cleanliness and health of the animals.
- Cleanliness of Milking Barns: Ensuring a hygienic environment for milk production.
- Disinfections: Regularly disinfecting the farm facilities to prevent the spread of diseases.
- Feeding Animals at Regular Intervals: Providing timely and balanced nutrition to the herd.
- Milking at Regular Intervals: Ensuring consistent and efficient milk extraction.
- Record Keeping: Meticulously documenting all farm activities and performance data.
Adhering to these routine operations is crucial for the overall well-being and productivity of the dairy herd.

Special Management Care for Animals
Different categories of animals require specific management practices to ensure their optimal health and performance:
1. Lactating Animals
- Colostrum Management: After calving, cows produce colostrum, a nutrient-rich milk that is crucial for the newborn calf’s development and immune system.
- Lactation Period: The ideal lactation period is 10 months (305 days), during which the cow should be provided with adequate nutrition to reach its full milking potential, particularly during the lactation peak.
2. Newborn Calves
- Navel Cord Disinfection: Disinfecting the navel cord with tincture iodine to prevent infections.
- Colostrum Feeding: Ensuring the calves receive the necessary antibodies and nutrients from colostrum.
- Assisted Suckling: Assisting if the calf is unable to suckle on its own.
- Housing and Weather Protection: Keeping calves in a dry, clean, and well-ventilated space, shielding them from extreme weather conditions.
- Grouping and Vaccination: Grouping calves according to size and administering necessary vaccinations.
- Dehorning: Dehorning calves around 4-5 days of age to prevent injuries.
- Disposal of Extra Calves: Responsibly disposing of extra calves not intended for rearing.
3. Pregnant Animals
Pregnant animals require special attention to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
4. Dry Cows
Dry cows, those not in milk, need proper management to prepare them for the next lactation cycle.
Implementing these specialized management practices for different animal categories can significantly enhance the dairy herd’s health, welfare, and productivity.

Reproduction Management
Efficient reproduction management is crucial for the profitability and sustainability of a dairy farm. Key aspects of reproduction management include:
- Heat Detection: Accurate heat detection is essential for timely insemination.
- Insemination: Ensuring timely and efficient insemination for successful conception.
- Pregnancy Diagnosis: Early pregnancy diagnosis allows for appropriate management of pregnant animals.
- Care of Pregnant Cows: Providing special attention to pregnant cows to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
- Post-Partum Reproductive Health Care: Proper post-partum care is essential for the cow’s health and future reproductive performance.
- Management of Repeat Breeding Cows: Cows that fail to conceive after repeated inseminations require special attention.
- Record Keeping of Breeding Cycles: Maintaining accurate records of breeding cycles for informed decision-making.
Effective reproduction management can enhance herd fertility, improve calving rates, and ultimately increase the overall productivity and profitability of the dairy farm.

Software for Dairy Herd Management
To assist with dairy herd management, several software programs are available, including:
- Merk Animal Health Pocket Dairy: A comprehensive dairy management application that helps farmers track herd health, reproduction, and productivity.
- Herdman: A cloud-based dairy management software that enables farmers to monitor and manage various aspects of their operations, from animal health to milk production.
Utilizing these specialized software solutions can enhance the efficiency and data-driven decision-making capabilities of dairy farmers.
Feeding Management
Cows are ruminants, with a four-compartment stomach, and their nutritional requirements are crucial for optimal milk production.
1. Nutrient Requirements
- Energy Requirement: 1800-31980 Kcal/day
- Total Digestible Nutrients (TDN): A balanced ration should contain 14-16% digestible crude protein (DCP) and 68-72% TDN.
- Dry Matter (DM): Cows require 2.5 kg of DM per 100 kg of body weight, with 2/3 from roughage and 1/3 from concentrates.
2. Concentrate Mix Composition
The table below shows an example of a concentrate mix composition:
| Ingredient | % | DCP in Ingredients | DCP in Ration | TDN in Ingredients | TDN in Ration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat/Maize (Cereals) | 33 | 7% | 2.31 | 80% | 26.40 |
| Groundnut cake/mustard cake/Till cake/Mug Chuni (Oil Cakes) | 33 | 38% | 12.54 | 73% | 24.09 |
| Rice Bran (Cereal by-products) | 33 | 10% | 3.33 | 66% | 21.78 |
| Salt/Min. Mix/Vitamin | 1 | – | – | – | – |
| GIVEN | – | 18.18 | 72.27 | ||
| RECOMMENDED (Minimum) | – | 14.00 | 68.00 |
3. Ration Calculation (Thumb Rule)
- Roughage: 3-4% of body weight (5-6 kg straw + 4-6 kg greens)
- Maintenance Ration: 2 kg concentrate per day
- Additional Ration: 500 gm concentrate per liter of milk production
For a cow producing 10 liters of milk daily, the total concentration requirement would be 7 kg (2 kg maintenance + 5 kg additional).
4. Fodder Cultivation
Cultivating fodder offers several advantages, including providing complete nutrition, enhancing milk quality, improving animal health and immunity, and reducing production costs. The article covers various types of perennial and seasonal grasses, as well as unconventional fodder like Azolla, that can be integrated into the feeding regime.
The article also addresses the current fodder scenario in West Bengal, where demand exceeds supply, and provides solutions to address this challenge, such as incentivizing fodder production, promoting unconventional fodder cultivation, and implementing intensive forage crop rotations.
Manure Management and Biogas Plants
Effective manure management through biogas plants can enhance dairy farm sustainability and optimize resource utilization. These systems convert cow dung into biogas, providing an alternative energy source while reducing the farm’s reliance on fossil fuels.
1. Biogas Plant Functionality
Biogas plants operate as anaerobic digesters, where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen to produce methane-rich biogas. Cow dung slurry is fed daily into the digestion tank, where this process occurs. The biogas generated can be used for cooking, heating, or electricity generation.
The byproduct of this digestion, known as spent slurry, is nutrient-rich and can be used as organic fertilizer for crops. This closed-loop system promotes sustainability by reducing waste and replacing chemical fertilizers with environmentally friendly alternatives.
2. Sizing Biogas Plants
| Biogas Plant Size (Cubic Meters) | Cow Dung Required (kg/day) | Number of Animals Supported |
|---|---|---|
| 2 cubic meters | 30-45 kg | 3-4 animals |
| 6 cubic meters | 80-100 kg | 7-10 animals |
Accurate sizing ensures that the plant produces enough biogas to meet the farm’s energy needs without being inefficient or overly costly.

Milk and Milk Products
Milk is a vital source of essential nutrients, with its composition varying across different breeds. Understanding milk’s nutritional makeup and processing methods is crucial for producing high-quality dairy products that are both safe and nutritious for consumers.
1. Milk Composition
Milk is a rich source of nutrients, and its composition varies depending on the breed of the animal. The article includes a table showcasing the variation in water, fat, protein, lactose, and ash content across different breeds, including Sahiwal, Gir, Holstein, Jersey, and Buffalo.
2. Milk Processing
The article outlines the basic milk processing operations, including:
- Raw Milk Collection: Milk is collected from farmers and stored in chilling plants.
- Transportation and Reception: Milk is transported to dairy plants using bulk coolers and received in silos.
- Milk Clarification: Solid impurities are removed through centrifugal force.
- Milk Separation: Fat is separated from raw milk using cream separators.
- Standardization: Fat and solid-non-fat percentages are adjusted to meet legal standards.
- Homogenization: Fat globules are broken down into smaller sizes for better digestion.
- Milk Pasteurization: Milk is heated to a specific temperature for a specific time to eliminate harmful bacteria and extend shelf life.
By understanding the intricacies of milk composition and processing, dairy farmers and industry stakeholders can ensure the production of high-quality, safe, and nutritious dairy products.
Conclusion
Effective dairy farm management requires a holistic approach that addresses all aspects of the operation, from animal selection and housing to feeding, reproduction, and milk processing.
By implementing best management practices, dairy farmers can enhance animal health and welfare, improve milk production and quality, and ultimately increase the profitability and sustainability of their dairy enterprises.
This article provides the necessary knowledge and insights to help dairy farmers and industry stakeholders optimize their operations and thrive in the dynamic dairy industry.
FAQs
1. What is the importance of dairy farm management?
Dairy farm management ensures the production of safe and high-quality milk products, protects animal welfare, preserves the environment, and enhances farm profitability and sustainability.
2. What are some common KPIs used in dairy farming?
Common Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) include average milk production per cow, calving interval, conception rate, calf mortality, and gross/net income.
3. What are some challenges in dairy farm management?
Key challenges include managing feed costs, maintaining high reproductive efficiency, ensuring animal health, and adapting to changing market conditions.
4. What resources are available for dairy farmers to improve their management practices?
Dairy farmers can access support from organizations such as the International Dairy Federation (IDF), extension services, universities, and industry publications. Michigan State University’s Dairy Management Program and the IDF offer valuable information, training, and guidance.